Arthritis: Symptoms, Causes, Types, Treatment, Diet & Complete Patient Guide
Nov 29, 2025
Arthritis is one of the most common joint conditions worldwide, affecting millions of people across all age groups. Many people think arthritis means “old age problem,” but the truth is that it can happen to anyone—young adults, middle-aged people, seniors, and even children. Arthritis simply means inflammation or swelling in the joints, which leads to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
If you experience joint pain, swelling, morning stiffness, or difficulty in movement, this detailed and easy-to-understand guide will help you understand what arthritis really is, why it happens, and how you can manage it effectively.
What is Arthritis?
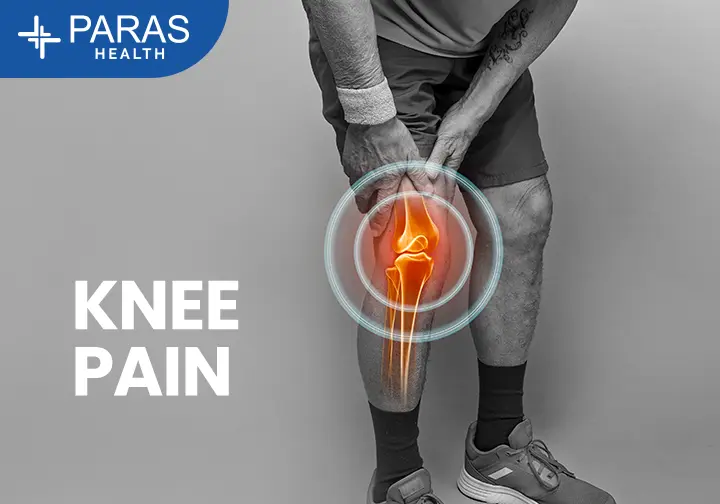
Arthritis refers to a group of conditions that cause joint pain, swelling, inflammation, stiffness, and reduced joint movement.
It is not just a single disease—there are 100+ types of arthritis.
The most common areas affected are:
- Knees
- Hips
- Hands
- Fingers
- Spine
- Shoulders
Arthritis can be mild, moderate, or severe. In some people, symptoms progress slowly, while in others they can worsen quickly.
Early Signs and Symptoms of Arthritis
Arthritis begins with small signs, but most people ignore them until pain increases.
Here are the most common symptoms:
Joint pain
Persistent pain in knee, hip, finger, or shoulder joints.
Joint stiffness
Especially after waking up in the morning.
Joint swelling and warmth
Swollen, red, or warm joints indicate active inflammation.
Reduced joint mobility
Difficulty bending knees, opening jars, or walking.
Tenderness
Pain when touching or pressing the joint.
Fatigue and weakness
Especially common in rheumatoid arthritis.
Types of Arthritis
Arthritis is not one condition—it has several types. Here are the major ones:
Osteoarthritis (OA) — “Wear and Tear” Arthritis
- Most common type
- Happens due to degeneration of joint cartilage
- Common in older adults, obese individuals, or after joint injuries
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) — Autoimmune Arthritis
- The immune system attacks the joints
- Causes severe inflammation
- Can affect both sides of the body (symmetrical)
Gout Arthritis
- Caused by increased uric acid
- Sudden, severe joint pain—mostly in the big toe
Psoriatic Arthritis
- Occurs in people with psoriasis
- Causes joint swelling, skin patches, and nail changes
Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Affects the spine
- Causes back stiffness, especially in the morning
Juvenile Arthritis
Arthritis in children below 16 years
Causes and Risk Factors of Arthritis
Arthritis can happen due to multiple reasons. The exact cause depends on the type.
Physical Causes
- Joint degeneration
- Wear and tear
- Previous joint injury
Medical Causes
- Autoimmune disorders
- Family history of arthritis
- Inflammatory diseases
Lifestyle Causes
- Obesity
- Lack of exercise
- Poor diet
- Repetitive strain on joints
Age-Related Factors
- Cartilage wears down with age
- Muscle and bone strength decline
Even environmental conditions like cold weather and humidity can make symptoms worse.
Diagnosis of Arthritis
A doctor may use several tests to confirm the type of arthritis:
Physical Examination
Checking swelling, pain, stiffness, and movement.
Blood Tests
- Rheumatoid Factor (RF)
- ESR & CRP (inflammation markers)
- Uric acid (for gout)
Imaging Tests
- X-ray: Shows joint damage
- MRI: Shows soft tissues, cartilage, ligaments
- Ultrasound: Detects inflammation in early stage
Early diagnosis helps slow the progression of arthritis significantly.
Treatment Options for Arthritis
Arthritis cannot always be “cured,” but it can be controlled and managed very well.
1. Medications
- Pain relief medications
- NSAIDs (anti-inflammatory drugs)
- Steroid injections
- DMARDs (for RA)
- Biologic therapy (in severe RA cases)
2. Physiotherapy
- Improves joint movement
- Reduces stiffness
- Strengthens muscles around joints
3. Lifestyle Modifications
- Weight loss reduces knee load
- Gentle movement and stretching
- Warm water bath
- Proper footwear
4. Surgical Treatment (for severe cases)
- Knee replacement
- Hip replacement
- Arthroscopy
Surgery is recommended only when pain becomes unmanageable and daily movement gets affected severely.
Arthritis Management: Complete Treatment Breakdown
|
Treatment Type |
What It Does |
When Used |
Benefits |
|
Pain Relief Medicines |
Reduces pain & swelling |
Mild–moderate pain |
Quick relief |
|
Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) |
Controls inflammation |
Active flare-ups |
Reduces stiffness |
|
Steroid Injections |
Strong anti-inflammatory action |
Severe joint pain |
Relief for weeks |
|
DMARDs (for RA) |
Controls immune activity |
Rheumatoid arthritis |
Slows joint damage |
|
Biologic Therapy |
Advanced immune treatment |
Severe RA |
High effectiveness |
|
Physiotherapy |
Strengthens muscles & mobility |
All arthritis types |
Increases movement |
|
Heat Therapy |
Relaxes stiff joints |
Morning stiffness |
Better flexibility |
|
Ice Therapy |
Reduces swelling |
After activity |
Calms inflammation |
|
Weight Management |
Reduces joint load |
Knee/OA |
Long-term benefit |
|
Assistive Devices |
Supports weak joints |
Elderly/severe cases |
Improves walking |
|
Surgical Treatment |
Replaces or repairs joints |
Severe arthritis |
Restores mobility |
Arthritis Diet: What to Eat & What to Avoid
Diet plays a major role in joint health and inflammation.
Foods That Reduce Arthritis Pain
- Omega-3 rich foods (walnuts, flaxseeds, chia seeds)
- Salmon, tuna (if non-veg)
- Turmeric + black pepper
- Ginger
- Green leafy vegetables
- Berries
- Olive oil
Foods to Avoid in Arthritis
- Red meat
- Deep-fried foods
- Packaged snacks
- Excess sugar
- Excess salt
- White bread and refined carbs
Helpful Supplements
- Vitamin D
- Calcium
- Omega-3 capsules
- Collagen supplements
Always take supplements under medical guidance.
Exercises for Arthritis and Joint Pain
Exercise keeps joints flexible and reduces pain.
Best Exercises
- Walking
- Cycling
- Swimming (best for joint pain)
- Yoga
- Stretching
- Strength training
Precautions
- Avoid heavy-impact exercises
- Warm up before starting
- Stop if sharp pain occurs
A physiotherapist can help create a personalized exercise plan.
Lifestyle Tips to Manage Arthritis Daily
- Maintain healthy weight
- Don’t sit for long hours
- Use heat and ice therapy appropriately
- Use ergonomic chairs, pillows, and braces
- Wear soft, supportive footwear
- Get good sleep
- Reduce stress—it worsens inflammation
Pain Management for Arthritis
- Heat therapy relaxes stiff joints
- Ice reduces swelling
- TENS therapy helps nerve pain
- Topical gels for quick relief
- Epsom salt warm water soaks
- Avoid overusing painful joints
Chronic pain should always be discussed with a specialist.
A Note from Paras Hospital
At Paras Hospital, we understand how joint pain affects your daily life—walking, climbing stairs, and even simple tasks can become challenging. Our dedicated team of Orthopaedic Specialists, Rheumatologists, Pain Experts, and Physiotherapists work together to ensure accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment.
We offer:
· Advanced arthritis treatment
· State-of-the-art physiotherapy
· Minimally invasive procedures
· World-class joint replacement surgeries
· Compassionate, patient-centered care
Whether your arthritis is mild or severe, early evaluation and timely treatment can prevent long-term joint damage. At Paras Hospital, we are committed to helping you regain mobility, comfort, and quality of life.
FAQs
What causes arthritis pain?
Arthritis pain occurs due to joint inflammation, cartilage damage, or increased pressure on the joint. Conditions like osteoarthritis, RA, and gout commonly cause long-term pain.
Is arthritis reversible?
Most types of arthritis cannot be fully reversed, but symptoms can be controlled. Early treatment, weight management, and physiotherapy help slow progression significantly.
Does walking help arthritis?
Yes, walking helps reduce stiffness, improves joint flexibility, and strengthens muscles. It should be done at a comfortable pace without overstraining the joints.
Which diet is best for arthritis patients?
An anti-inflammatory diet rich in omega-3 foods, leafy vegetables, fruits, nuts, and whole grains is best. Avoid fried foods, sugar, and processed snacks for better joint health.
Can arthritis be cured naturally?
Arthritis cannot be completely cured naturally, but symptoms can be improved through exercise, weight loss, turmeric, ginger, and a clean anti-inflammatory diet.
How do I stop arthritis from getting worse?
Maintain a healthy weight, exercise regularly, avoid joint overuse, take medications on time, and follow a joint-friendly routine. Early treatment prevents long-term damage.
What are early signs of arthritis?
Morning stiffness, joint swelling, pain during movement, and reduced flexibility are common early signs. These symptoms worsen with age or lack of activity.
Which medicine is best for joint pain?
Pain relievers, NSAIDs, and anti-inflammatory medicines work well. For autoimmune arthritis, DMARDs and biologics may be prescribed by a doctor.
Can arthritis be prevented?
Yes, to some extent. Regular exercise, maintaining ideal weight, eating an anti-inflammatory diet, and avoiding joint injuries can reduce your risk.
When should I see a doctor for joint pain?
If pain lasts more than 2 weeks, swelling increases, or daily activities become difficult, consult a doctor. Early diagnosis prevents long-term joint damage.