Blogs
- All
- Cardiac Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology & Cosmetology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- ENT, Neck & Head Surgery
- Gastro Sciences
- General Surgery
- Internal Medicine
- Neuro Sciences
- Obstetrics & Gynaecology
- Onco Care
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Plastic Surgery
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Renal Sciences
- Emergency
- Urology
- Liver Transplant & GI Surgery
- Dietetics & Nutrition
- General
Internal Medicine | Post Date : Feb 27, 2026
Iron deficiency in women is one of the most common nutritional problems worldwide. Yet, many women ignore early signs like fatigue, hair loss, weakness, or dizziness, thinking it’s just stress or a busy lifestyle.
Continue Reading
Dietetics & Nutrition | Post Date : Feb 26, 2026
Heart disease remains one of the leading health concerns worldwide. High cholesterol, high blood pressure, diabetes, obesity, and stress are major contributors. The good news? Your daily diet plays a powerful role in prevention.
Continue Reading
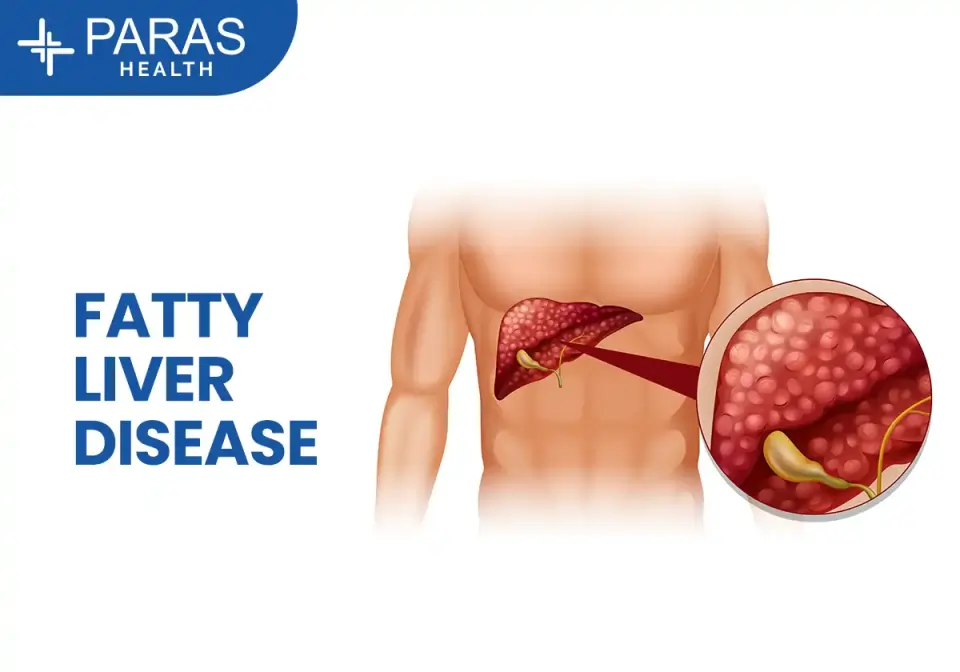
Gastro Sciences | Post Date : Feb 26, 2026
Fatty Liver Disease is becoming one of the most common lifestyle-related health problems today. Earlier, liver diseases were mostly linked to alcohol consumption, but now even young adults and people who do not drink alcohol are being diagnosed with fatty liver.
Continue Reading
Dietetics & Nutrition | Post Date : Feb 24, 2026
Managing diabetes does not mean giving up Indian food. In fact, the right Indian diet for diabetes control can help you stabilize blood sugar levels, improve energy, and prevent long-term complications.
Continue Reading
Onco Care | Post Date : Feb 23, 2026
Breast cancer in women is one of the most common cancers worldwide. But the most important thing to remember is this — early detection of breast cancer saves lives. When breast cancer is diagnosed at an early stage, treatment is more effective and survival rates are significantly higher.
Continue Reading
Endocrinology | Post Date : Feb 21, 2026
Have you recently been told that your blood sugar levels are slightly high, but not high enough to be called diabetes? If yes, you may have prediabetes.
Continue Reading