Symptoms & Diagnosis of Ependymoma
Apr 19, 2022
Basically people with ependymoma are diagnosed for the disease only once the symptoms surface. Symptoms may start to surface slowly in this condition. A common diagnostic test that identifies potential neurologic problems is a magnetic resonance image or MRI.
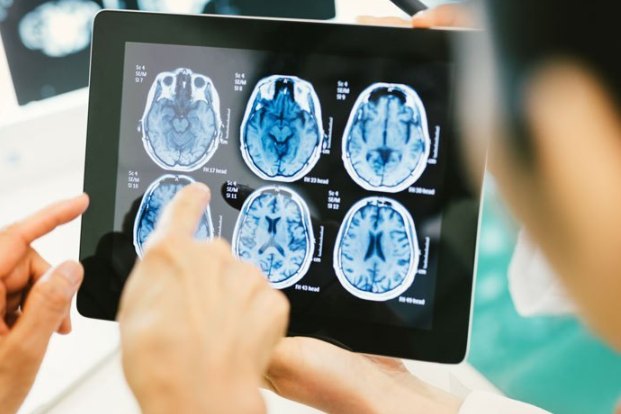
Other times, problems occur basically and result in an urgent trip to an emergency room or clinic. An exam by a health care provider often shows neurologic problems. A common diagnostic test that identifies potential neurologic problems is a magnetic resonance image or MRI. An MRI is typically the preferred test for people who may have a brain or spinal cord tumor. It shows a better picture of the brain, spine and tumor than computed tomography (CT) scans, although a CT scan may be the first test that is done. This is mainly because ependymoma tumors do not tend to spread outside of the central nervous system (CNS). MRI of the brain or spine is not only used as a baseline test, but may also be used to evaluate the whole central nervous system.
Symptoms of ependymoma are follows:-
- Neck pain
- Headaches
- Vision changes, such as blurred vision or vision loss
- Jerky eye movements
- Nausea and vomiting
- Difficulty with balance or walking
- Seizures and convulsions
- Weakness in the limbs
In rare cases, an ependymoma can spread. Before starting any treatment, the doctor will first want to know if there are any other tumours in the brain or spine. For this reason, a number of tests are done at diagnosis to see if the cells have spread. Ependymomas are classified according to grade. In the brain, ependymomas are either grade 2 or 3. Grade 2 ependymomas are also called benign. Grade 3 ependymomas are also called malignant.
Following tests may be used to diagnose ependymoma:
- Computed tomography (CT or CAT) scan.A CT scan takes pictures of the inside of the body using x-rays taken from different angles. A computer combines these pictures into a detailed, 3-dimensional image that shows any abnormalities or tumors. A CT scan can be used to measure the tumor’s size.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).An MRI uses magnetic fields, not x-rays, to produce detailed images of the body. MRI can be used to measure the tumor’s size.
- A biopsy is the removal of a small amount of tissue for examination under a microscope. Other tests can suggest that a tumor is present, but only a biopsy can make a definite diagnosis. A pathologist then analyzes the sample(s). A pathologist is a doctor who specializes in interpreting laboratory tests and evaluating cells, tissues, and organs to diagnose disease. For ependymoma, surgery is needed to get a sample of tissue (see Types of Treatment).
- Lumbar puncture (spinal tap).A lumbar puncture is a procedure in which a doctor uses a needle to take a sample of cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) to look for tumor cells









