Brain Stroke Symptoms: Early Warning Signs You Should Never Ignore
Jul 18, 2025
A brain stroke can happen in seconds, but its effects can last a lifetime. The good news? Acting fast can save a life—and reduce long-term damage. The first step is knowing what to look out for.
In this blog, we’ll walk you through the early brain stroke symptoms, how to recognize a stroke in men, women, and the elderly, and when to seek urgent medical help. Whether you're a caregiver, family member, or just someone who wants to stay prepared—this guide is for you.
What Is a Brain Stroke?
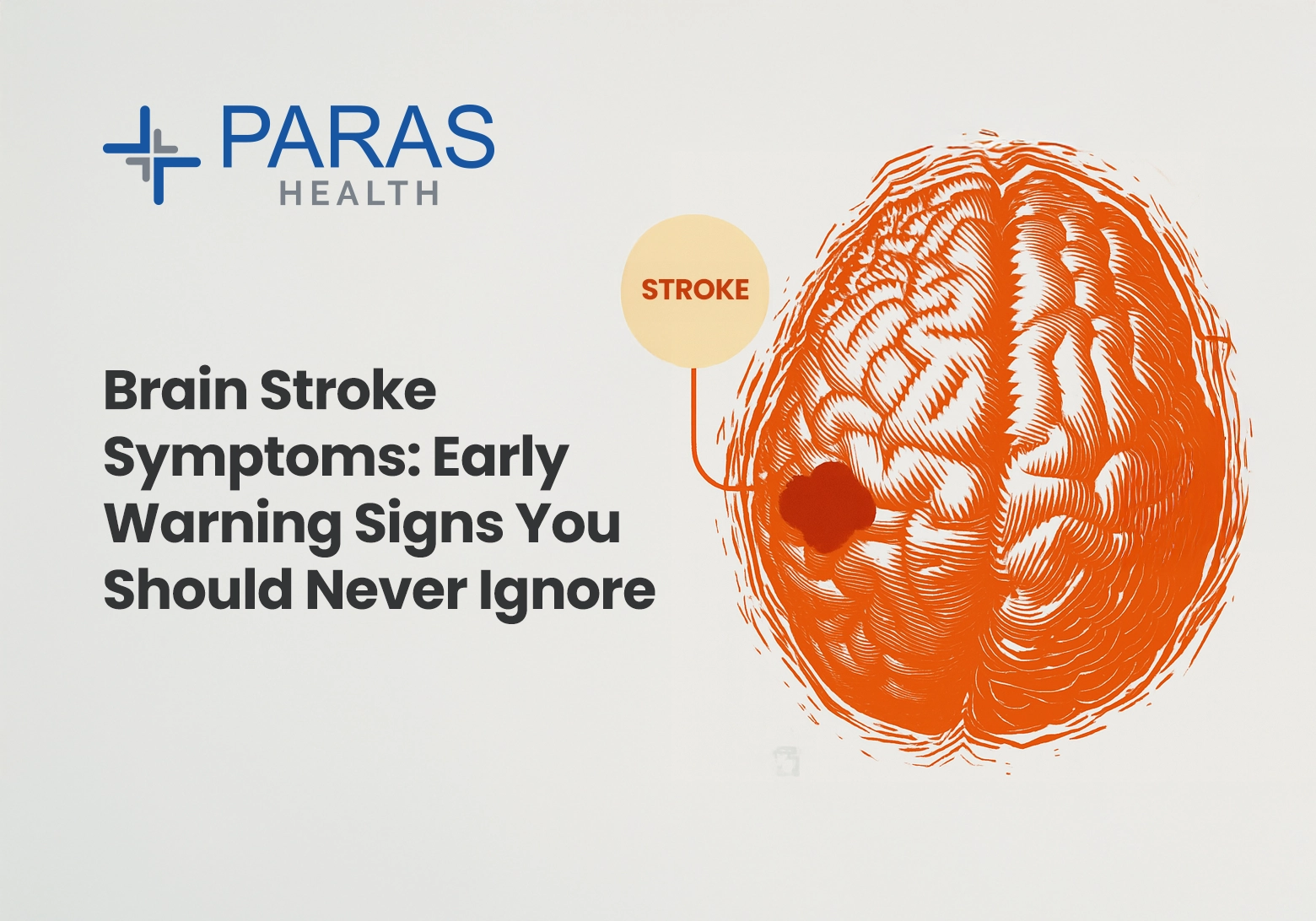
A brain stroke happens when the blood supply to a part of the brain is blocked or a blood vessel bursts, damaging brain tissue. This medical emergency is also known as a brain attack.
There are mainly two types of strokes:
- Ischemic Stroke: Caused by a blood clot blocking a brain artery (most common).
- Hemorrhagic Stroke: Caused by bleeding in or around the brain due to a ruptured blood vessel.
- There’s also TIA (Transient Ischemic Attack), often called a mini-stroke, which is temporary but a serious warning sign.
No matter the type, early detection is key.
Why Recognizing Symptoms Early Is Critical
The golden rule in stroke care is: Time = Brain.
Every minute after a stroke, the brain loses nearly 2 million nerve cells. Delaying treatment can lead to:
- Permanent brain damage
- Loss of movement or speech
- Long-term disability
- Even death in severe cases
So, knowing the early signs of stroke can make all the difference.
Brain Stroke Symptoms to Watch Out For
1. Sudden Numbness or Weakness
- Especially on one side of the body—face, arm, or leg.
- You may notice a drooping smile or an inability to lift one arm.
2. Confusion or Trouble Speaking
- Slurred speech
- Difficulty understanding others
- Sudden loss of ability to form words
This is one of the most common and alarming stroke symptoms.
3. Vision Problems
- Blurred, double, or sudden loss of vision in one or both eyes.
- May feel like a “curtain” coming down over your eyesight.
4. Loss of Balance or Coordination
This is more common in stroke in elderly individuals.
5. Sudden Severe Headache
- Especially without any clear reason
- Can be a sign of hemorrhagic stroke
- May come with vomiting or loss of consciousness
6. Sudden Fatigue or Fainting
- Feeling lightheaded, confused, or faint
- May happen with or without other stroke symptoms
Who Is at Higher Risk of Stroke?
While strokes can happen to anyone, the risk is higher in:
- People over age 60
- People with high blood pressure or diabetes
- Smokers or heavy alcohol consumers
- Those with high cholesterol
- People with heart disease or irregular heartbeat (AFib)
- People who’ve had a mini-stroke (TIA) before
Even young adults and women can have strokes. In women, symptoms may include sudden hiccups, chest pain, or shortness of breath, making them harder to recognize.
How to Recognize Stroke FAST
Here’s a simple way to spot a stroke quickly—remember the F.A.S.T. rule:
- F – Face: Is one side of the face drooping?
- A – Arms: Can the person raise both arms?
- S – Speech: Is speech slurred or strange?
- T – Time: Time to call emergency help immediately!
Even if symptoms disappear in a few minutes (common in TIA or mini-stroke), it’s still a medical emergency.
What to Do If You Notice Stroke Symptoms
- Call emergency services immediately.
- Do not wait to see if symptoms improve.
- Note the time symptoms began—it helps doctors decide the best treatment.
- Do not give the person food, drink, or medication unless directed by a doctor.
The faster a stroke patient gets to a hospital, the better their chances of recovery.
🔄 Stroke vs Migraine vs Seizure
People often confuse stroke symptoms with migraines or seizures.
|
Condition |
Key Feature |
|
Stroke |
Sudden weakness, speech issues, one-sided body effects |
|
Migraine |
Visual aura, throbbing headache, usually no paralysis |
|
Seizure |
Jerky body movements, unconsciousness, tongue biting |
If in doubt—always assume it’s a stroke and act fast.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: How do I know if I’m having a stroke?
Look for sudden symptoms like one-sided weakness, confusion, slurred speech, or vision loss. Use the FAST test to confirm.
Q2: What does a mini stroke feel like?
A TIA (mini stroke) feels like a stroke but lasts only a few minutes. Even though it goes away, it’s a serious warning sign.
Q3: Can a stroke happen suddenly?
Yes, most strokes happen suddenly, without any warning. That’s why early detection is critical.
Q4: What should I do if I suspect someone is having a stroke?
Call emergency services immediately. Don’t delay, even if symptoms seem mild.
Q5: Are stroke symptoms different in women?
Women may experience unique symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath, nausea, or fainting, in addition to common signs.
Q6: Can stress cause a stroke?
While stress doesn’t directly cause a stroke, chronic stress can increase blood pressure and risk of stroke over time.
Q7: Can a stroke be prevented?
Yes, managing blood pressure, diabetes, quitting smoking, exercising, and eating healthy can reduce your stroke risk.
Conclusion: Don’t Ignore the Warning Signs
A brain stroke doesn’t always come with pain, but it’s always an emergency. Recognizing the early signs of stroke—slurred speech, facial drooping, vision loss, or arm weakness—can help you or your loved one get timely care and avoid serious disability.
If you or someone around you experiences even one of these symptoms, don’t wait. Call emergency services or rush to the nearest stroke treatment hospital.
Being aware today could save a life tomorrow.