Arthritis- A Guide To Patients
Apr 19, 2022
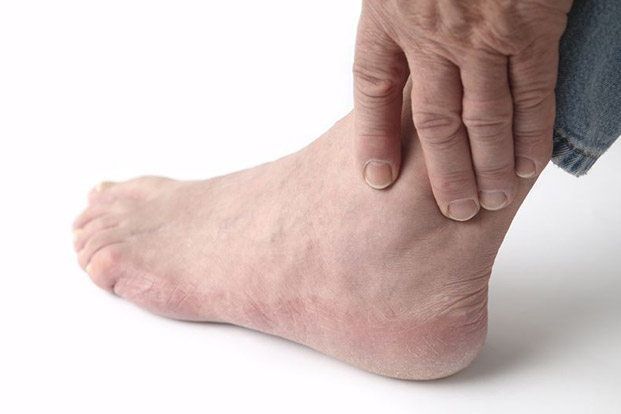
Arthritis is the Inflammation of one or more joints, causing pain and stiffness that can worsen with age. It affects almost all age groups most commonly the elderly and every joint of body is affected. There are over 100 identified (and the number is growing) types of arthritis. It ranges from those related to wear and tear of cartilage – osteoarthritis to those associated immune mediated inflammation – rheumatoid arthritis. It may also include acute ,short duration or chronic pain.
Majority of arthritis are inherited to some degree, there is no real way to prevent them. However can be prevented by life style modifications, losing excess weight, abiding to safety regulations to avoid becoming injured, by not becoming infected with the causative organism, etc.
Diagnosis of Arthritis:
Diagnosis of arthritis includes – physical exam- swelled, warm or red joints, and limited range of motion, grating feeling in the joints. Blood and joint fluids determine the kind of arthritis.
Imaging scans such as X-ray, CT and MRI scans are used to rule out other causes.
There is no cure for arthritis (except gout). The main goal of treatment is to reduce the amount of pain and prevent additional damage to the joints
Treatment of Arthritis:
- Life style modifications include morning walk, posture correction, relaxation techniques, etc.
- Physical therapy involving exercises and deep heat therapies that help strengthen the muscles around the affected joint.
- Medication includes – analgesics – (hydrocodone or acetaminophen): Effective for pain management, but don’t help decrease inflammation-
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) – ibuprofen: help control pain and inflammation
- Menthol or capsaicin creams: Block the transmission of pain signals from your joints
In case of RA(rheumatoid arthritis), corticosteroids or disease-modifying anti rheumatic drugs (DMARDs),is used.
- Surgery-
- Osteotomy: Realignment of deformed joints .
- Replacement surgery: Replacement of native destroyed joint with an artificial one most commonly performed on hips and knees.
- Joint fusion: In case of small joints of hands and occasionally for large joints
Community and family plays a vital role in long term treatment and care of arthritic patients as financial and emotional support heals the disease more than medicines.









